A State transition diagram describing a part of Yeast Cell Cycle Biology Diagrams This will also help you to draw the structure and diagram of cell structure of yeast. The yeasts are unicellular fungi. Cells may remain attached in short chains forming a pseudomycelium, but they do not produce true mycelium. The cells are extremely variable in shape being globose, oval, elongated, or rectangular.

Interestingly, Delobel et al., [32] used FCM to quantify the relative proportions of yeast cells in each cell cycle stage at different points of the growth curve of a population in batch culture
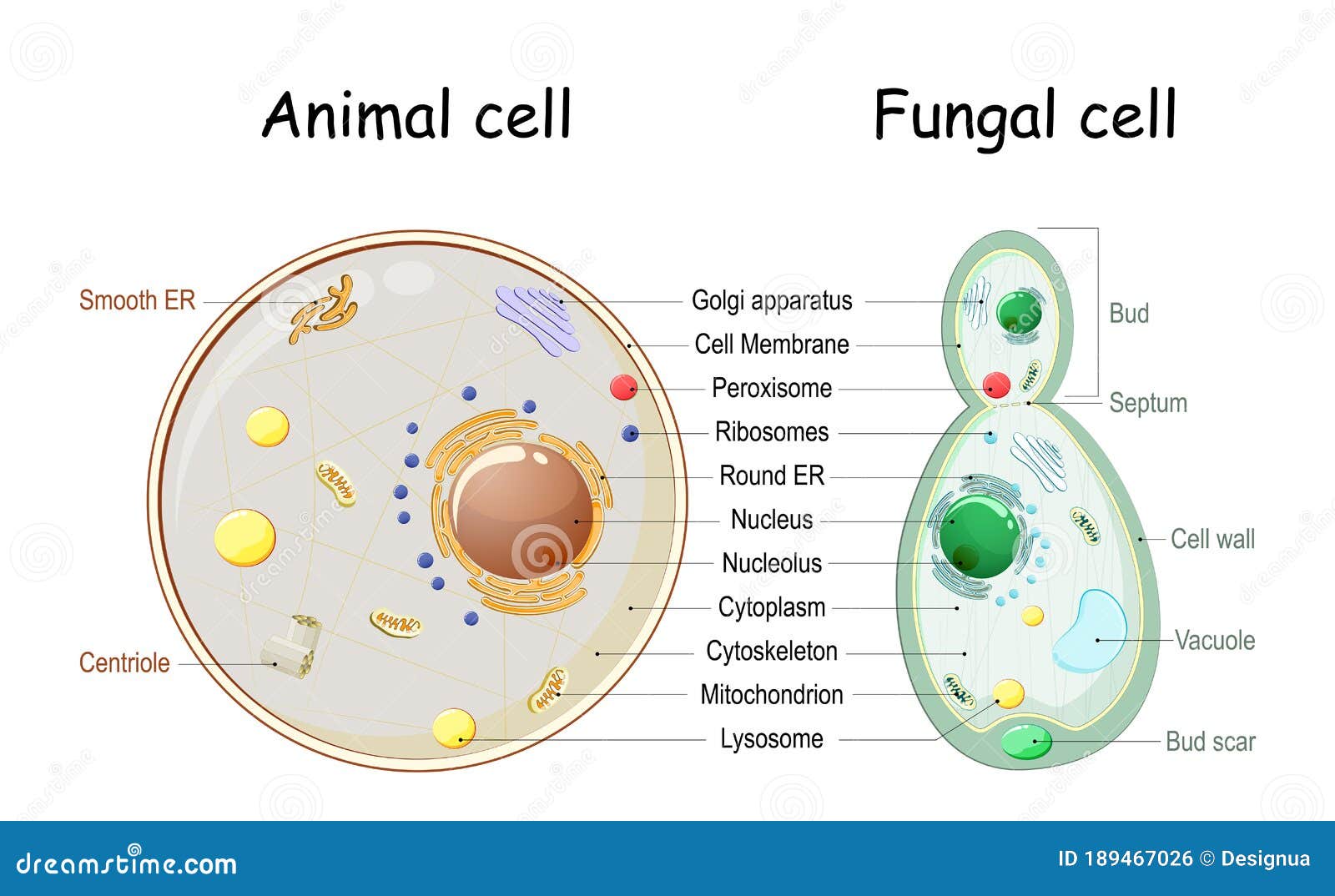
Yeast: morphology and life cycle Biology Diagrams
Yeast: morphology and life cycle. They are single celled fungi; Size: generally larger than most bacteria; (1-5) um wide and (5-30)um length; Shape: cell is egg shaped, some are elongated or spherical; Size and shape varies among species; Yeast cell lacks flagella and other organ of locomotion. Morphology of yeast cell

(B) The yeast cell cycle diagram shows the phases of the cell cycle. The abbreviations used for yeast cell cycle stand for the standard terms: 1 M, Mitosis; S, Synthesis; G 1 and from publication
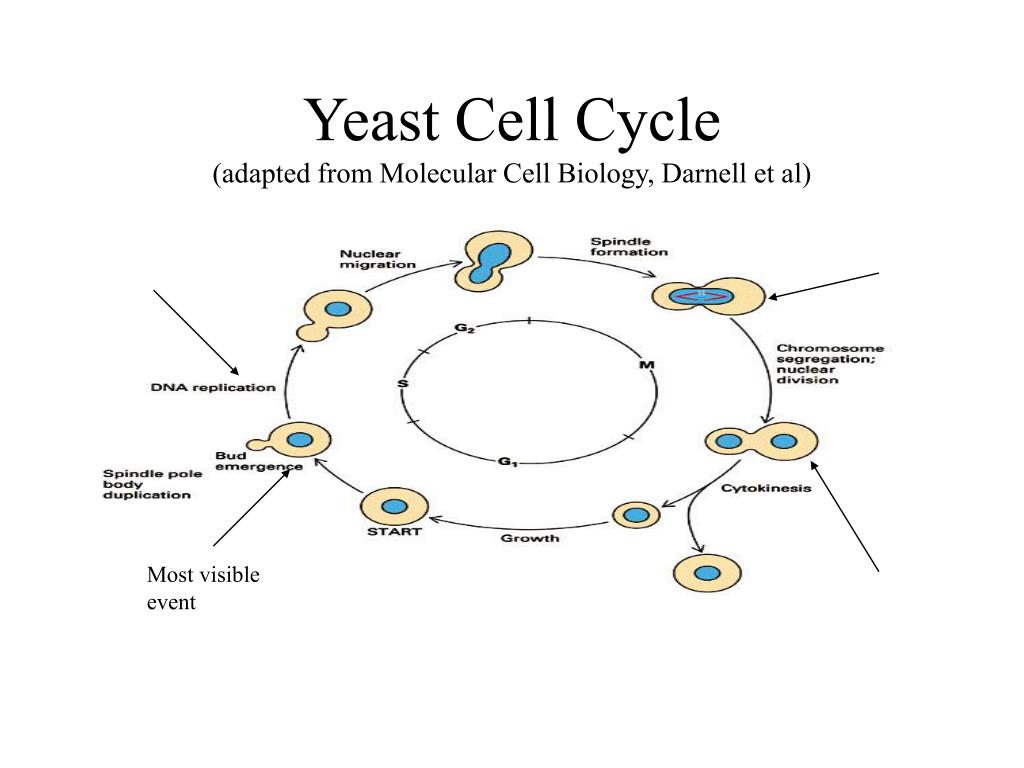
PDF Cell Cycle of BY vignette Biology Diagrams
Understanding the Yeast Cell Cycle. As in all living organisms, yeast cells undergo a cycle of growth and division called the cell cycle. The yeast cell cycle consists of four main phases: Gap1 (G1), Synthesis (S), Gap2 (G2), and Mitosis (M). In the G1 phase, the yeast cell prepares to duplicate its DNA and initiates the synthesis of proteins ADVERTISEMENTS: The below mentioned article provides an overview on the cell structure of yeast. Antony Von Leeuwenhoek (1680) was the first to describe the yeast cells. Its thallus is unicellular and non-mycelial. However, at the time of budding it rarely produces pseudo-mycelium. The individual cells are polymorphic i.e., showing different shapes, even in the same […]
